Ethereum 2.0, or Eth2, represents a crucial upgrade to the existing Ethereum blockchain, aiming to enhance speed, efficiency, and scalability. This transformative upgrade builds upon the current network, addressing longstanding issues to unlock new potentials for decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Eth2 introduces significant improvements, ensuring a more robust and versatile platform for users and developers. It reflects the Ethereum community’s commitment to innovation and progress, setting the stage for a future where decentralized applications can thrive. This strategic evolution marks a pivotal moment in Ethereum’s history, transitioning from previous limitations to new possibilities.

The Genesis of Ethereum 2.0
The Ethereum network, since its inception, has operated on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which, while secure, has faced criticism for its energy-intensive nature and scalability limitations. Ethereum 2.0 is set to transition the network to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, a move that promises to drastically reduce energy consumption and enhance the network’s ability to process transactions.
The upgrade is occurring in multiple phases, with the first phase, the Beacon Chain, already live since December 1, 2020. The Beacon Chain introduces native staking to the Ethereum network, laying the groundwork for the upcoming phases. The anticipated second phase, “the Merge,” is scheduled for the second quarter of 2022, marking the integration of the Beacon Chain with the current Ethereum mainnet. Following this, the final phase will launch shard chains, vastly expanding the network’s capacity by distributing operations over 64 new chains.
Ethereum 2.0: A New Name for a New Era
In January 2022, the Ethereum Foundation initiated a rebranding campaign, shifting from the terminology “Ethereum 2.0.” They aimed to highlight the upgrade as an enhancement and continuation of the existing Ethereum network, not the creation of a new one. In this new terminology, the existing network becomes the “execution layer,” hosting smart contracts and network rules, while “Ethereum 2.0” becomes the “consensus layer,” ensuring adherence to protocols by network participants.
Despite the rebranding, many still commonly use the term “Ethereum 2.0,” reflecting the upgrade’s transformative impact and its potential to redefine the Ethereum network’s capabilities.
The Journey to Ethereum 2.0
The transition to Ethereum 2.0 is a monumental task, unfolding in several carefully planned phases, each contributing unique enhancements to the network.
The Beacon Chain: Laying the Foundation of Ethereum 2.0
Launched on December 1, 2020, the Beacon Chain marked the first phase of Ethereum 2.0. It operates parallel to the existing Ethereum network, introducing the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism to the Ethereum ecosystem. In this new paradigm, validators replace miners, staking ETH as collateral to validate transactions and create new blocks. This shift not only reduces the network’s energy consumption but also sets the stage for subsequent phases of Ethereum 2.0.
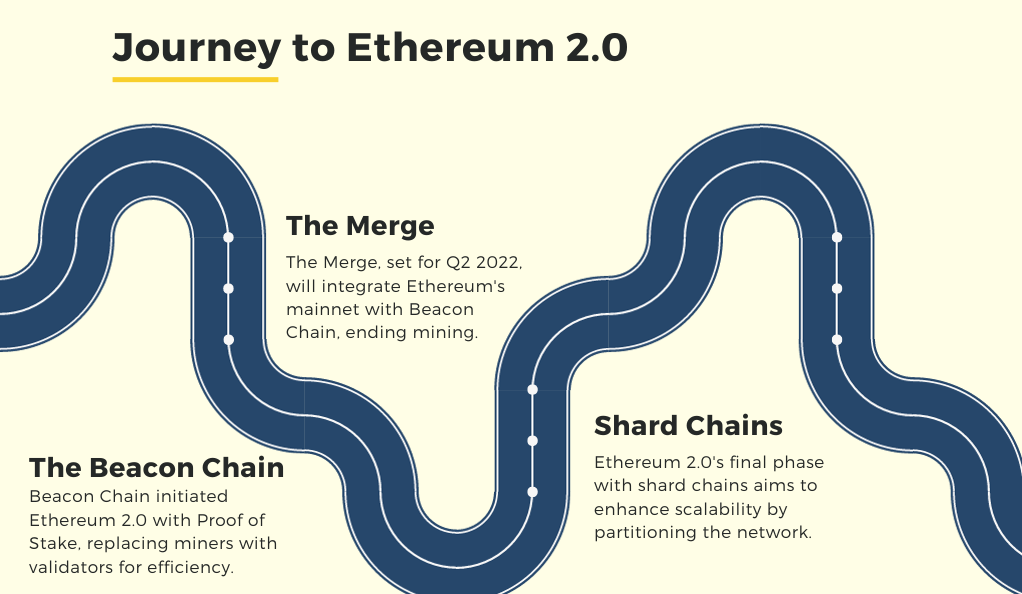
The Merge: Unifying Layers
Anticipated in the second quarter of 2022, the Merge represents a pivotal moment in the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. During this phase, the Beacon Chain will merge with the existing Ethereum mainnet, transitioning the network’s consensus mechanism from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake. This merger signifies the full integration of the new consensus mechanism, marking the end of energy-intensive mining on the Ethereum network.
Shard Chains: Enhancing Scalability
The final phase of Ethereum 2.0 introduces shard chains, a solution designed to address the scalability issues of the Ethereum network. Currently, every transaction and smart contract execution requires the consensus of the entire network, leading to bottlenecks and limited scalability. Shard chains propose to distribute the load, partitioning the network into 64 new chains that can process transactions and smart contracts in parallel. This innovation promises to significantly increase the network’s capacity and speed, accommodating a much larger volume of transactions.
From Proof of Work to Proof of Stake
The Ethereum network is undergoing a transformative shift in its consensus mechanism, moving from the energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) to the more efficient Proof of Stake (PoS). This change is central to the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, aiming to address the scalability and environmental concerns associated with the traditional mining process.
In a PoW system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems, with the first to succeed adding a new block to the blockchain and receiving a reward in the network’s native cryptocurrency. While this process secures the network, it requires immense computational power and energy, leading to concerns about its sustainability and efficiency.
The Advantages of Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake presents a method that is more energy-efficient compared to traditional models. In this system, network participants have the opportunity to become validators by locking in a specific amount of cryptocurrency. The selection of validators to create new blocks and validate transactions depends on the quantity of their stake and the duration of their holdings. This method, often referred to as “forging” or “minting,” substantially lowers the network’s energy consumption by separating the consensus mechanism from the need for extensive computational power.
Security and Decentralization of Ethereum 2.0
In addition to its environmental benefits, PoS offers enhanced security and decentralization. Ethereum 2.0 requires a minimum of 16,384 validators, ensuring a wide distribution of control and reducing the risk of centralization. This large number of validators also enhances the network’s resilience against attacks, making it more secure than networks with fewer validators.
The transition to Proof of Stake is a critical component of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, promising a more sustainable, secure, and scalable blockchain network. In the following section, we will explore how these changes contribute to the scalability of the Ethereum network, enhancing its capacity to handle a larger volume of transactions and smart contracts.
Scalability and Performance Enhancements
One of the primary motivations behind the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is to address the network’s scalability issues, ensuring it can efficiently handle a growing volume of transactions and smart contracts. The introduction of shard chains plays a crucial role in achieving this goal, promising a future where the Ethereum network can seamlessly scale to meet demand.
The Limitations of Ethereum 1.0
In its current state, the Ethereum network can process approximately 30 transactions per second. This limitation stems from the need for every transaction to be processed by the entire network, leading to bottlenecks and delays during periods of high demand. As the popularity of decentralized applications and smart contracts continues to grow, these scalability issues become increasingly pronounced.
Shard Chains: A Scalability Solution
Shard chains are a novel solution introduced in Ethereum 2.0 to overcome these limitations. By partitioning the network into 64 new chains that can process transactions and smart contracts in parallel, shard chains enable a significant increase in the network’s capacity. This parallel processing capability allows the Ethereum network to handle a much larger volume of transactions, potentially scaling up to 100,000 transactions per second.
A More Efficient Network
The implementation of shard chains not only enhances the network’s scalability but also improves its overall efficiency. Validators are assigned to specific shard chains, ensuring that the workload is evenly distributed and that each chain operates optimally. This distribution of labor reduces the hardware requirements for running an Ethereum node, making it more accessible and further decentralizing the network.
Enhancing Security and Decentralization of Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 2.0 brings with it significant improvements in security and decentralization, addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring a more robust network. These enhancements are crucial for maintaining user trust and facilitating the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
A More Decentralized Network
In traditional Proof of Work networks, the high computational power required to mine blocks can lead to centralization, as only those with significant resources can participate. Ethereum 2.0, with its Proof of Stake consensus mechanism, lowers the barrier to entry, allowing a more diverse group of participants to become validators. This diversity enhances the decentralization of the network, distributing control more evenly and reducing the risk of centralization.
The mandate of having at least 16,384 validators guarantees a broad dispersion of control across the network, bolstering its resilience and security. This substantial number of validators serves to decentralize the network and fortify its defenses, making it increasingly challenging for malicious entities to seize control.
Enhanced Security Measures
Ethereum 2.0 introduces several security measures to protect the network and its participants. Validators are required to stake a significant amount of ETH, which can be forfeited in the event of malicious behavior or negligence. This staking mechanism acts as a financial deterrent, encouraging validators to act in the best interest of the network.
Additionally, the introduction of shard chains reduces the potential impact of a single point of failure. By spreading transactions and smart contracts across multiple chains, the network ensures that an issue in one shard does not compromise the entire system.
Preparing for the Future
These security and decentralization enhancements are not just about addressing current issues; they are also about future-proofing the Ethereum network. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and find new applications, the need for a secure and decentralized network becomes increasingly important. Ethereum 2.0 lays the groundwork for this future, ensuring that the network remains resilient, secure, and decentralized, no matter how it is used.
Economic and Price Implications of Ethereum 2.0
The shift to Ethereum 2.0 represents more than a mere technical enhancement; it also carries substantial ramifications for Ethereum’s economic framework, with the potential to impact the value of Ethereum itself and affect the wider cryptocurrency market.
Potential for Increased Demand and Price
The enhancements in scalability, security, and efficiency brought about by Ethereum 2.0 are expected to lead to increased adoption and usage of the Ethereum network. As more users and developers flock to the platform, the demand for Ethereum is likely to rise, which could, in turn, drive up the price.
Additionally, the upgrade strives to lower transaction fees and enhance transaction speeds, tackling two significant challenges faced by users and developers. By making these improvements, the Ethereum network could become a more appealing platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts, potentially boosting demand and contributing to an increase in value.
Staking and Its Economic Implications
With the introduction of Proof of Stake, Ethereum holders now have the opportunity to stake their ETH and become validators, earning rewards for their participation in the network. This staking mechanism could lead to a reduction in the circulating supply of Ethereum, as more users lock up their ETH to earn rewards. A decrease in supply, coupled with increased demand, could create upward pressure on the price.
Nonetheless, it is crucial to consider the new economic dynamics introduced by staking in Ethereum 2.0. Validators must commit a substantial amount of ETH, potentially impacting Ethereum’s liquidity and volatility. As the rollout of Ethereum 2.0 progresses, close monitoring of these factors will be essential.
Long-Term Bullish Outlook with Short-Term Volatility
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade casts a generally bullish long-term projection for Ethereum, even in the face of the cryptocurrency market’s well-known volatility. Particularly during this significant network transition, it is prudent to expect short-term price fluctuations. Nevertheless, amidst this instability, a multitude of industry experts and stakeholders maintain a positive outlook on Ethereum’s future and the beneficial influence of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. They view the improvements in scalability, security, and efficiency as essential strides towards maturing the network, securing its ongoing relevance and success in the fast-paced realm of blockchain and cryptocurrency.
The Future and Roadmap of Ethereum 2.0
As Ethereum 2.0 continues to unfold, the future of this ambitious upgrade is a topic of much anticipation and speculation. The roadmap laid out by the Ethereum Foundation and community developers provides a glimpse into the ongoing developments and the long-term vision for Ethereum.
Continuous Development and Optimization
The journey to Ethereum 2.0 is a multi-phase process, with each phase introducing new features and improvements. Even after the completion of the major phases, the development team will continue to optimize and enhance the network, ensuring it remains secure, efficient, and scalable. This continuous improvement is crucial for maintaining the network’s competitiveness and relevance in the ever-evolving blockchain landscape.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions and Ethereum 2.0
In addition to the core developments of Ethereum 2.0, there is a growing ecosystem of layer 2 scaling solutions, such as rollups, that are designed to work alongside the upgrade to further enhance scalability and performance. These solutions aim to offload some of the transactional load from the main Ethereum chain, providing faster and cheaper transactions.
The integration and interoperability of these layer 2 solutions with Ethereum 2.0 are a key focus for developers, ensuring that users and developers can seamlessly take advantage of the combined benefits of both layers.
The ultimate goal of Ethereum 2.0 is to create a decentralized, secure, and scalable blockchain platform that can serve as the foundation for a new generation of decentralized applications and services. The upgrade is a significant step towards realizing this vision, providing the necessary infrastructure and features to support a decentralized and inclusive digital economy.
The Ethereum community and developers are actively working towards this future, with a clear roadmap and a commitment to continuous improvement. As Ethereum 2.0 continues to evolve, it promises to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of blockchain technology and decentralized systems.
Conclusion
Ethereum 2.0 marks a significant turning point in blockchain development, bringing substantial enhancements in terms of scalability, security, and efficiency. With the ongoing rollout of this upgrade, the Ethereum network is set to transform into a stronger, more decentralized, and accessible platform, ready to accommodate diverse applications and services. Looking ahead, Ethereum 2.0 shines with potential, paving the way towards a secure and decentralized digital future.

